Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults. You may also hear it referred to as “juvenile diabetes”. About 5 percent of people with diabetes have type 1. In patients with type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that the body needs to get glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of the body. Therefore, these patients must take insulin by injection or via insulin pump in order to manage their blood glucose levels.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas can still make insulin, but your body does not use insulin properly. This is called insulin resistance. Initially, the pancreas makes extra insulin to try to overcome the resistance. But, over time it isn't able to keep up enough to keep your blood glucose at normal levels. Some patients with type 2 diabetes can be managed strictly through dietary modifications and exercise, however many require medication to control the diabetes. This may include oral medication, injectable medications other than insulin, insulin, or a combination of several medications.
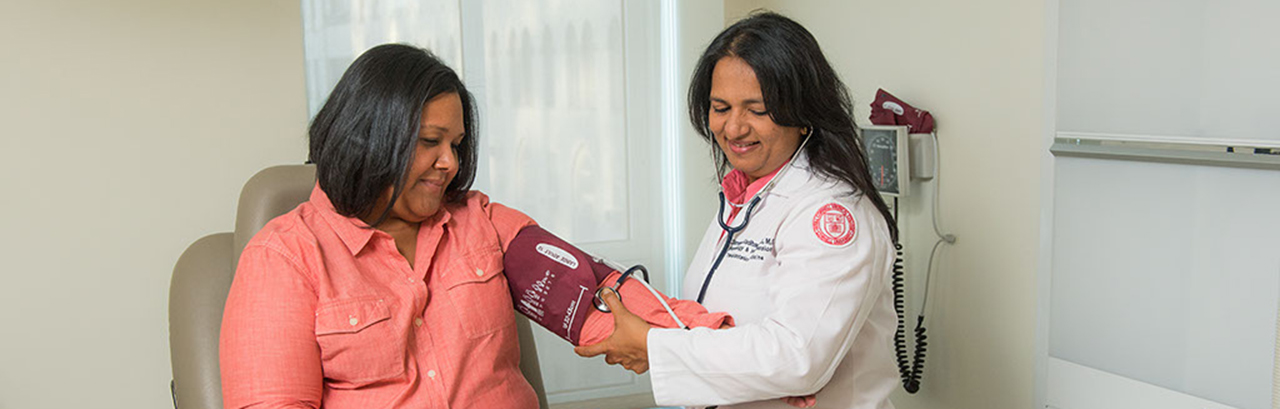
Diabetes and Kidney Disease: Regardless of the type of diabetes, poor control of blood glucose levels can lead to diabetes-related complications including kidney disease (nephropathy), eye problems (retinopathy), nerve problems (neuropathy), and heart and vascular (blood vessel) issues.
Related Treatments