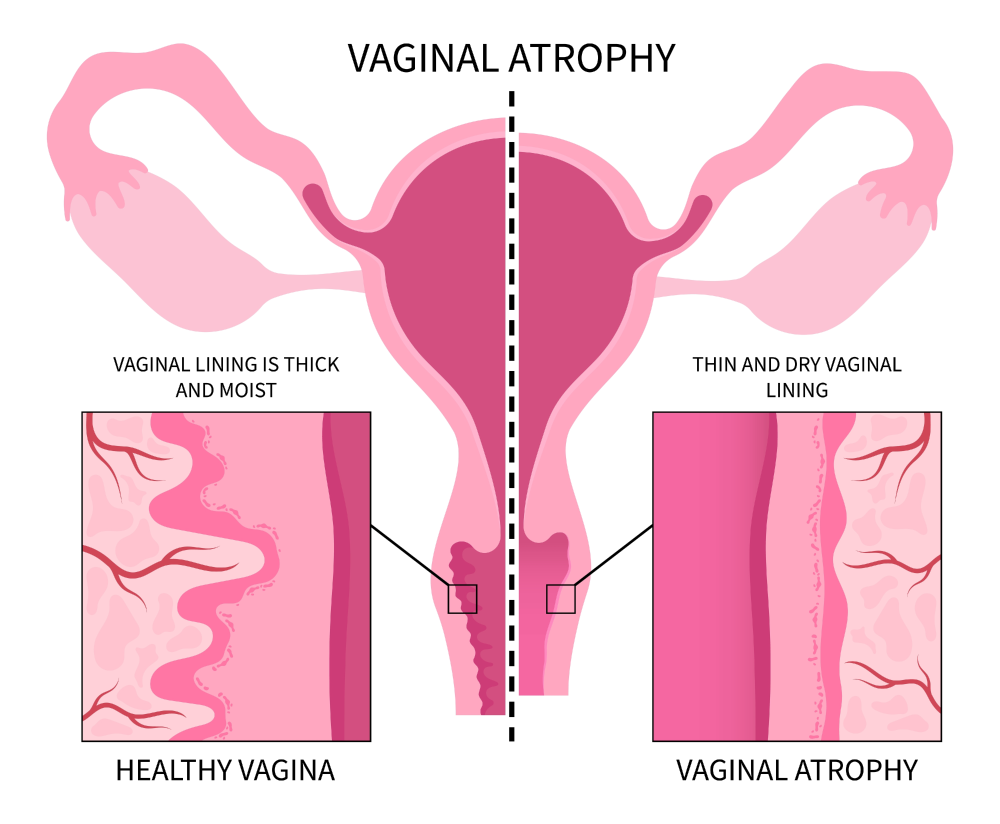
Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GUSM), also known as vaginal atrophy, urogenital atrophy or atrophic vaginitis, refers to changes in the vagina and urethra due to declining estrogen levels in these tissues. As a result of the drop in estrogen these tissues become weakened, thinner, and drier. These symptoms present when women are peri- or postmenopausal.
Common symptoms of GUSM include:
Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause typically occurs due to declining estrogen levels in menopause. However, decreased estrogen stimulation of urogenital tissue can also occur in premenopausal women. A decrease in estrogen can also be caused by treatment from surgery, radiation, or hormonal treatment, specifically for breast cancer.
There is no way to prevent Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause as it is a result of decreasing estrogen levels with menopause. However, topical vaginal estrogen can be used to manage the symptoms.
Since there are a variety of conditions that may cause the symptoms associated with Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause, it is recommended that patients with such complaints see a doctor for further evaluation. A patient history intake will be conducted along with a physical examination for any presenting physical signs.
If diagnosed with GUSM or vaginal atrophy, the most effective treatment for urogenital atrophy is low-dose vaginal estrogen replacement. This topical estrogen comes in a variety of preparations including a cream, suppository and intravaginal ring. It is important to be aware that low-dose vaginal estrogen replacement is not the same as systemic estrogen replacement therapy used to treat hot flashes and bone loss.
Other hormonal treatments:
To request an appointment, please call our office at (646) 962-7400 or schedule an appointment with one of our providers online below. Our phone staff are available to help you Monday-Friday, from 9AM-5PM (EST).
Meet our expert providers who specialize in treating Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause: