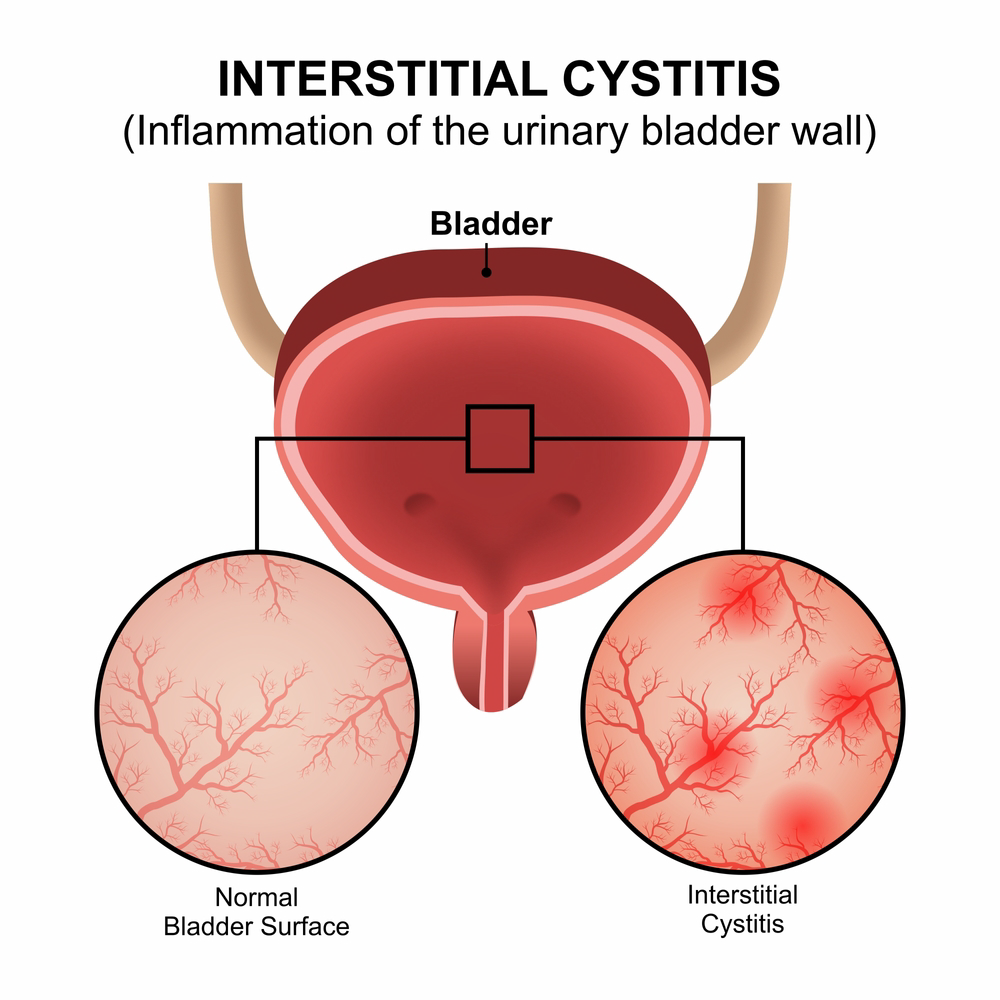
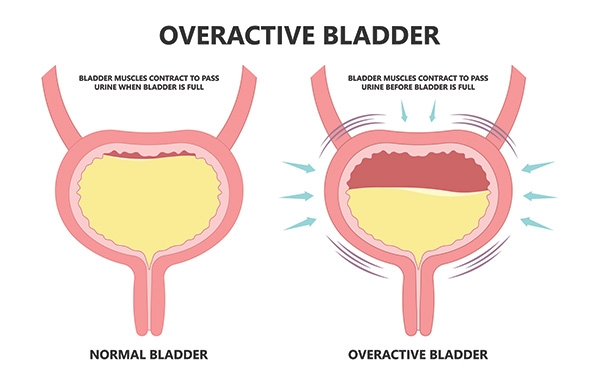
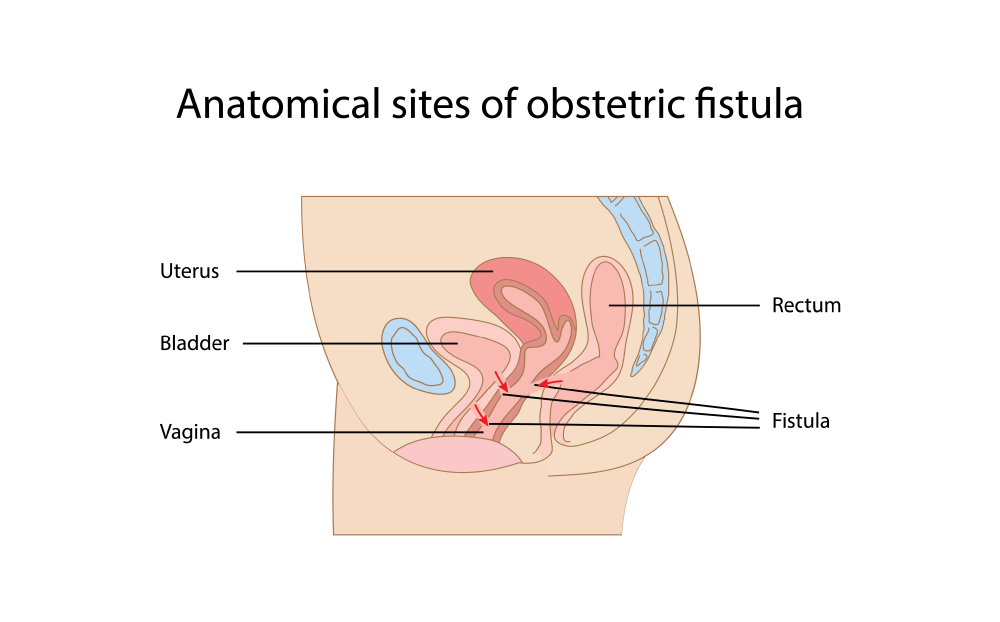
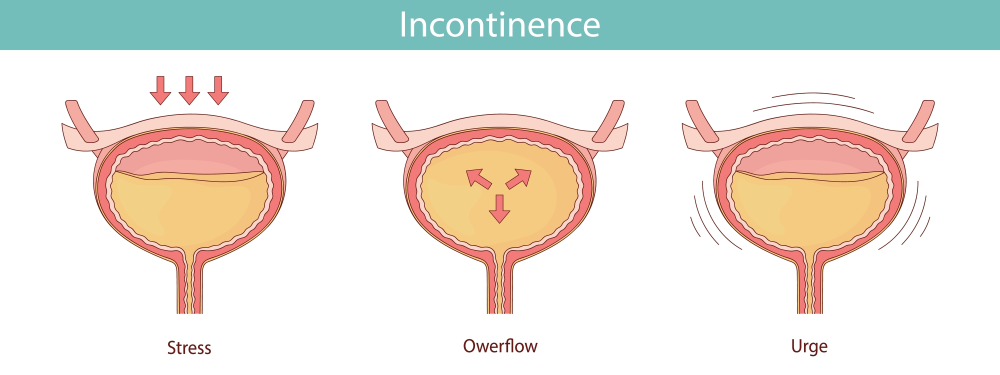
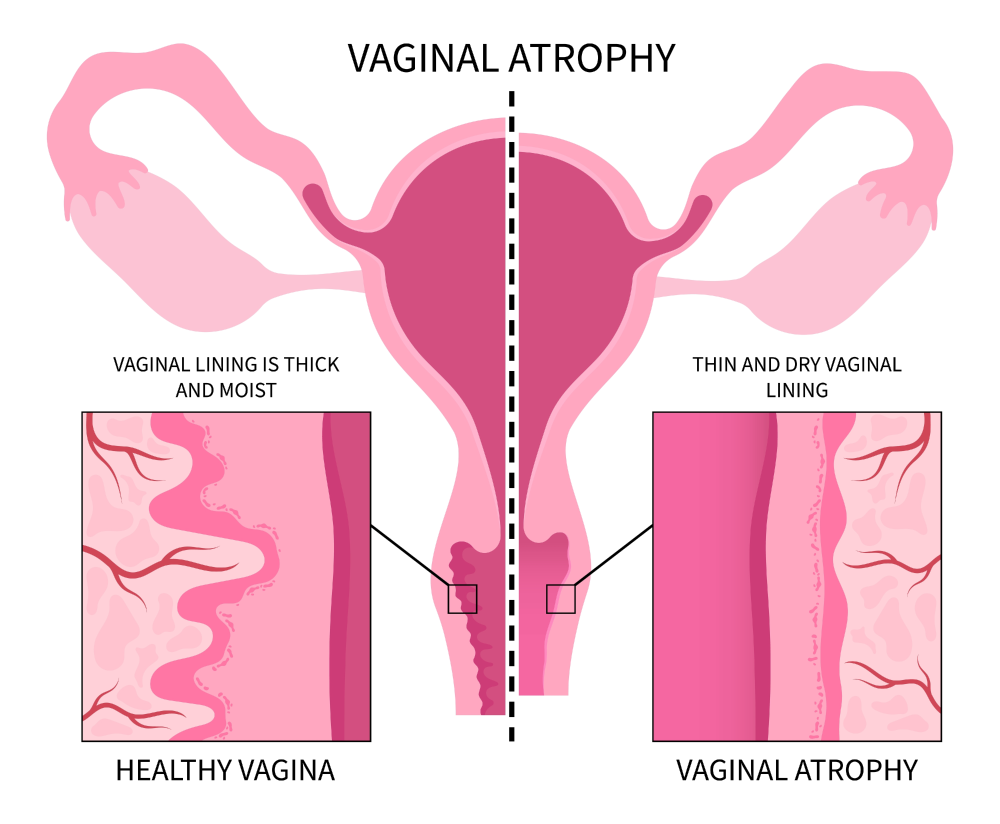
When pelvic organs, such as the bladder or uterus, drop into the vaginal canal, it can cause a noticeable bulge from the vaginal opening, pelvic pain or pressure or difficulty emptying the bladder and/or rectum. Nonsurgical treatment options for pelvic organ prolapse include Kegel exercises, pelvic floor therapy or vaginal pessary. Surgical treatment options include native tissue repair or robotic/laparoscopic prolapse repairs.
 Related Treatments
Related Treatments